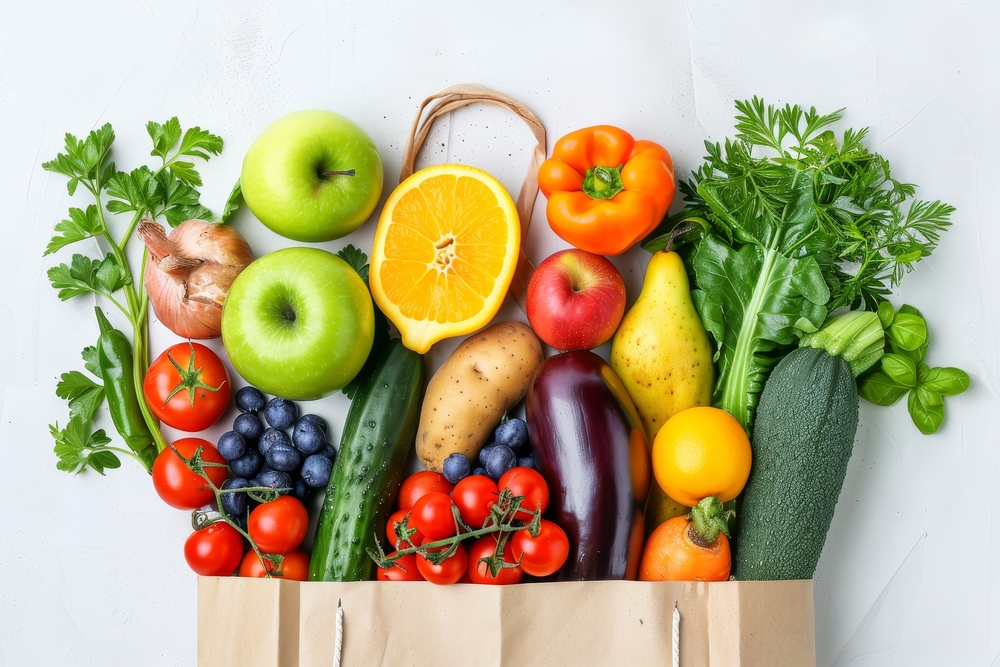
Inflammation is a natural response of the body’s immune system, but when it becomes chronic, it can lead to various health issues, including arthritis, heart disease, and digestive disorders. At CanStrive MedSpa & Wellness Clinic in Mississauga, ON, we’re dedicated to supporting whole-body health and well-being, which often begins with the right diet. Here’s a closer look at foods known to help fight inflammation, aiding your body in maintaining a balanced immune response and promoting long-term wellness.
1. Colorful Berries: Antioxidant-Rich Powerhouses
Berries like strawberries, blueberries, and raspberries are packed with antioxidants, specifically anthocyanins, which help reduce inflammation in the body. These antioxidants work to neutralize free radicals—unstable molecules that can damage cells and lead to chronic inflammation. Regularly consuming berries is associated with lower levels of inflammatory markers in the blood, such as C-reactive protein (CRP). They’re also an excellent source of fiber and vitamins, which further support immune function.
Incorporate berries into your diet by adding them to smoothies, oatmeal, or simply enjoying them as a refreshing snack. Frozen berries are just as nutritious as fresh ones, so you can have a supply on hand year-round.
2. Leafy Greens: Nutrient-Dense Choices for Cellular Health
Leafy greens like kale, spinach, and Swiss chard are loaded with vitamins, minerals, and fiber, which work collectively to reduce inflammation and support cellular health. These vegetables contain vitamin K, an essential nutrient for blood clotting and bone health, which has also been linked to lowering inflammatory markers in the body.
The fiber in leafy greens also promotes a healthy gut, which plays a central role in regulating inflammation. Incorporate a variety of greens in your meals, whether through salads, green smoothies, or as side dishes.
3. Fatty Fish: Omega-3 Fatty Acids to Combat Inflammation
Fatty fish, including salmon, mackerel, sardines, and trout, are rich in omega-3 fatty acids, essential fats that have powerful anti-inflammatory effects. Omega-3s, particularly eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), reduce the production of molecules and substances linked to inflammation, like cytokines and eicosanoids.
Aim to include fatty fish in your diet at least twice a week to help lower inflammation and support cardiovascular health. For those who are not fans of fish, fish oil supplements can be a beneficial alternative. Just be sure to consult with a healthcare provider before adding any supplements to your routine.
4. Turmeric: Nature’s Anti-Inflammatory Spice
Turmeric, a golden-hued spice commonly used in curries, contains curcumin, an active compound celebrated for its strong anti-inflammatory properties. Studies have shown that curcumin blocks certain molecules involved in inflammation pathways, offering similar benefits to some anti-inflammatory drugs but without the side effects.
Adding turmeric to your diet can be as simple as incorporating it into soups, stews, or smoothies. Curcumin is more effectively absorbed by the body when combined with black pepper, so be sure to add a pinch of pepper to maximize its benefits.
5. Nuts and Seeds: A Nutrient-Packed Snack for Fighting Inflammation
Nuts like almonds, walnuts, and seeds such as chia and flaxseeds are excellent sources of healthy fats, fiber, and antioxidants. Walnuts, in particular, are high in alpha-linolenic acid (ALA), a type of omega-3 fatty acid that has been shown to reduce inflammation.
These foods also contain magnesium, a mineral linked to lower inflammation levels, as well as fiber, which promotes a healthy digestive system and regulates immune responses. Incorporate nuts and seeds into your diet by adding them to salads, yogurt, or enjoying them as a standalone snack.
6. Green Tea: A Calming, Anti-Inflammatory Beverage
Green tea is rich in polyphenols, especially epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG), which are antioxidants known for their anti-inflammatory effects. Research suggests that regular green tea consumption can reduce the risk of heart disease, certain cancers, and other conditions related to chronic inflammation.
Swapping out sugary beverages for green tea is a simple, effective way to incorporate this anti-inflammatory powerhouse into your routine. To get the most benefits, aim for two to three cups of freshly brewed green tea each day.
7. Olive Oil: The Heart-Healthy Anti-Inflammatory Oil
Extra virgin olive oil is a staple of the Mediterranean diet and is rich in monounsaturated fats and oleocanthal, an antioxidant with effects similar to ibuprofen. Regular consumption of olive oil has been shown to reduce inflammation markers, which can support heart and joint health.
Drizzle olive oil over salads, use it as a cooking oil at low to medium temperatures, or enjoy it as a dip for whole-grain bread. When choosing olive oil, opt for extra virgin varieties to maximize its health benefits.
8. Tomatoes: Versatile and Anti-Inflammatory
Tomatoes are an excellent source of lycopene, a potent antioxidant that has been linked to reducing inflammation in the body, particularly in relation to certain cancers. Cooking tomatoes increases the lycopene content, making tomato sauces, soups, and stews fantastic options for your anti-inflammatory diet.
Incorporate tomatoes into meals by adding them to salads, sandwiches, or pasta dishes. Whether fresh or cooked, tomatoes offer a versatile and accessible way to support an anti-inflammatory lifestyle.
9. Garlic and Ginger: Flavorful and Anti-Inflammatory
Garlic and ginger not only add flavor to dishes but also contain compounds with powerful anti-inflammatory effects. Allicin, found in garlic, has been shown to combat inflammation and support immune health. Ginger, on the other hand, contains gingerol, a substance that helps reduce inflammation, pain, and swelling.
Use garlic and ginger generously in cooking or prepare a warm tea with fresh ginger to help soothe inflammation from the inside out. Both spices make an easy addition to most savory dishes, boosting flavor while supporting health.
10. Whole Grains: Fiber-Rich Foods for Gut and Immune Health
Whole grains like brown rice, quinoa, and oatmeal provide fiber, which supports a balanced gut microbiome. A healthy gut is essential for a balanced immune system, and research shows that a fiber-rich diet can reduce inflammation and improve immune function. Unlike refined grains, which can contribute to inflammation, whole grains provide essential nutrients like magnesium and B vitamins that support cellular health and fight inflammation.
Incorporate whole grains into your daily meals as a replacement for refined grains, helping to stabilize blood sugar levels and promote overall health.
Embracing Anti-Inflammatory Foods in Your Everyday Life
Introducing these anti-inflammatory foods into your diet doesn’t have to be complicated or restrictive. At CanStrive MedSpa & Wellness Clinic in Mississauga, we encourage a balanced approach that suits your lifestyle and dietary preferences. By making gradual, mindful changes to include more of these nutrient-dense foods, you’re taking an essential step toward reducing inflammation and promoting long-term wellness. Not only can these dietary changes support your physical health, but they can also improve mood, energy levels, and resilience over time.
Sources
- Johnson, M., & Ahmed, N. (2020). The Role of Omega-3 Fatty Acids in Inflammation. Journal of Nutrition Research.
- Lee, K., & Park, E. (2019). Curcumin as an Anti-Inflammatory Agent: Mechanisms and Clinical Applications. Nutritional Reviews.
- Brown, L., & Williams, G. (2021). Polyphenols and Inflammation: Mechanisms and Potential Benefits. International Journal of Food Sciences.